How to Rock a 3D CAD Modeling Workflow That Will Save You Tons of Time
- GigHz
- February 18, 2025
- emi and emc
- Home
- Email Us

3D CAD Model
Time is the universal currency.
We use time.
We save time.
However, time is a finite resource, and eventually, we all reach a point where it runs out.
As the saying goes, “Live as if today is your last day on earth,” reminding us of the importance of valuing the time we have and living with purpose.
In the automotive industry, especially when designing battery enclosures for electric vehicles (EVs), time-saving directly impacts efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall productivity.
A battery enclosure is a critical component in the design of electric vehicles (EVs), serving as the protective casing that shields the battery from external elements and internal hazards.
In the world of automotive design, the importance of these enclosures has only grown as electric vehicles become more advanced and more widely adopted.
Not only do they help maintain optimal battery performance, but they also ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of the vehicle’s power system.
The primary role of a battery enclosure is to protect the battery from physical damage and environmental conditions such as moisture, dust, or extreme temperatures.
These conditions can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of the battery if not properly managed.
Additionally, battery enclosures are designed to manage the thermal characteristics of the battery pack.
Why is it important to consider 3d modeling?
MCAD 3D modeling is crucial in PCB design for ensuring accurate component placement and clearance, preventing mechanical conflicts, and optimizing thermal management through heat dissipation simulations.
It also enhances structural integrity by analyzing stress and strain, integrates seamlessly integrates with ECAD for synchronized designs, and facilitates virtual prototyping to reduce costs.
Additionally, it ensures manufacturability through DFM and DFA analysis and improves communication with stakeholders by providing detailed technical documentation and 3D visualizations.
How to Rock a MCAD 3D Modeling Workflow That Will Save You Tons of Time?
1. Define Design Requirements:

- Objective: Understand the technical and environmental requirements for the battery enclosure.
- Details: This includes defining parameters such as size constraints, weight restrictions, thermal management needs, and safety standards (e.g., crash resistance and protection from environmental elements like water and dust).
- Tools/Software: Use tools like product requirement management systems or initial design brief documents to gather and define these parameters.
2. Conceptual Design:
- Objective: Develop multiple design concepts for the battery enclosure.
- Details: At this stage, conceptual sketches or rough 3D models are created to explore different form factors, material choices, and cooling solutions. The focus is on ensuring that the design accommodates the battery pack and other EV components (e.g., cooling systems, electrical connections) effectively.
- Tools/Software: MCAD tools such as SolidWorks, CATIA, or Autodesk Inventor can be used to generate initial 3D models.
3. Detailed 3D Modeling:
- Objective: Develop a detailed 3D model of the battery enclosure.
- Details: Using MCAD tools, the conceptual design is transformed into a more accurate 3D model. This includes adding features such as mounting points, cooling channels, connectors, and structural reinforcements. The model will also account for how the enclosure fits within the EV’s chassis.
- Tools/Software: SolidWorks, CATIA, Siemens NX, or PTC Creo for precise 3D modeling.
4. Thermal Simulation and Analysis:

- Objective: Ensure proper thermal management within the battery enclosure.
- Details: Once the 3D model is created, it is subjected to thermal simulations to assess heat dissipation. In EVs, battery packs generate heat, which can impact performance and longevity. The goal is to optimize airflow or integrate cooling systems (e.g., liquid cooling or heat sinks) to keep the battery temperature within safe operating limits.
- Tools/Software: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software like ANSYS Fluent or Siemens Simcenter can simulate heat distribution and cooling effectiveness.
- Stress and Structural Analysis:
- Objective: Validate the strength and durability of the enclosure.
- Details: Structural simulations are performed to test how the enclosure performs under various stresses, such as vibrations during driving, impacts, and accidents. This ensures the enclosure can withstand environmental and physical forces without compromising battery safety.
- Tools/Software: Finite Element Analysis (FEA) tools such as ANSYS Mechanical or Abaqus can be used for stress and structural analysis.
- Material Selection:
- Objective: Select materials that balance strength, weight, and cost.
- Details: Material selection is critical for optimizing the performance of the battery enclosure. Engineers will choose materials based on factors such as thermal conductivity, strength, corrosion resistance, and weight. Common materials include aluminum, steel, or composite materials.
- Tools/Software: Materials selection tools in MCAD software can help optimize material choices based on the design specifications.
7. Prototype Development:
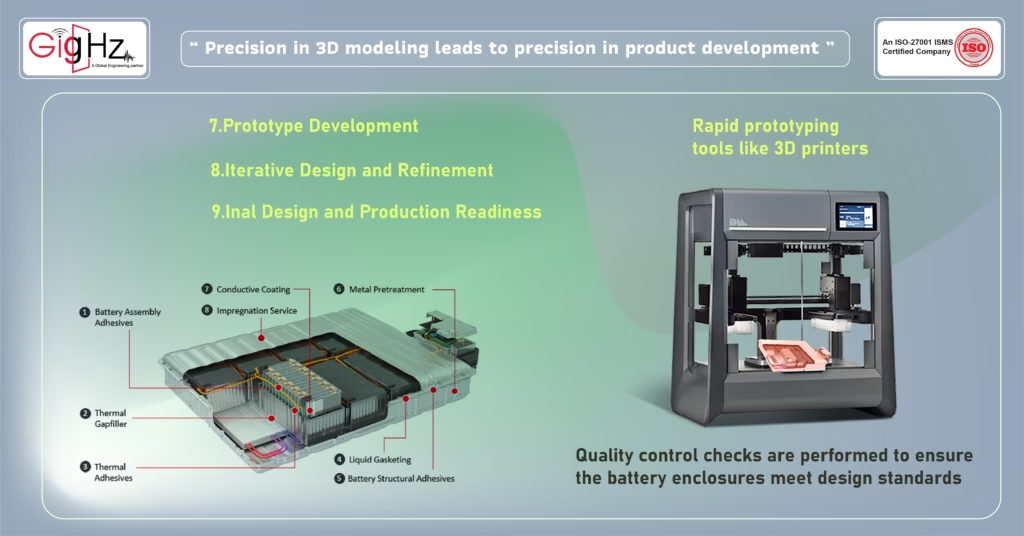
- Objective: Create a physical prototype for testing and validation.
- Details: Once the 3D model and simulations are complete, a physical prototype of the battery enclosure is manufactured (using 3D printing or CNC machining). This prototype is then tested under real-world conditions to ensure all performance requirements are met.
- Tools/Software: Rapid prototyping tools like 3D printers or CNC machines, and advanced manufacturing technologies like additive manufacturing.
- Iterative Design and Refinement:
- Objective: Refine the design based on test results.
- Details: After testing the prototype, engineers will identify any issues or improvements needed, such as adjustments to cooling channels, strength enhancements, or ergonomic changes. The design will go through multiple iterations to refine and perfect it.
- Tools/Software: Continuous use of MCAD software to make adjustments and improvements, followed by further simulations and tests.
- Final Design and Production Readiness:
- Objective: Prepare the design for mass production.
- Details: Once the design is finalized, it is handed over to the manufacturing team. At this stage, the design files are prepared for manufacturing, and tooling for mass production is set up.
- Tools/Software: MCAD tools generate the necessary manufacturing documentation, including 2D drawings, assembly instructions, and CAD files for the production line.
- Quality Control and Production Monitoring:
- Objective: Ensure that the manufactured battery enclosures meet all specifications.
- Details: During the production phase, ongoing quality control checks are performed to ensure the battery enclosures meet design standards. This may include inspections, testing, and validation of the final products.
- Tools/Software: Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) and quality control software.
Summary
By following this step-by-step workflow, engineers can create battery enclosures for electric vehicles that not only meet safety and performance standards but also leverage cutting-edge MCAD 3D modeling to optimize the design for manufacturability, efficiency, and sustainability.
Optimizing your MCAD 3D modeling workflow can significantly improve efficiency, particularly in complex automotive applications like battery enclosures for electric vehicles.
For deeper insights, check out our latest updates on LinkedIn https://www.linkedin.com/in/chandra-thimma/recent-activity/all/
Latest Post
Get Customized Engineering CAD Design Service

Book a Free Consultation Call
Partner with Gighz and bring your most innovative design concepts to life. Our engineering cad services accelerate development so you can focus on your big vision.
