What is EMC Testing in Automotive Electronics?
Most of today’s road vehicles rely on active devices, microprocessors, and vehicle communication networks for control of vehicle functions, entertainment systems, and legislated requirements such as tire pressure monitoring. Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) represents a device’s capacity to operate accurately while curbing unintended electromagnetic noise emission and countering external electromagnetic interference (EMI). EMC in automotive testing evaluates the ability of automotive electronics to withstand electromagnetic disturbances, such as radio frequency interference from other vehicle systems, electrical components, or external sources, while also ensuring that they don’t emit excessive electromagnetic immunity that could interfere with other vehicle systems or external devices.

Imagine a world where drawing a picture on a computer screen could turn into real things. That’s what Mechanical Computer-Aided Design, or MCAD, does. It’s like magic for engineers and designers. In this digital adventure, we’ll see how MCAD helps create amazing machines and gadgets. You don’t need to be a genius; you just need a computer and some ideas.
Category :
Published Date :
November 17, 2023
Category :
Published Date :
November 17, 2023
Category :
Published Date :
November 17, 2023
Automotive EMC testing evaluates the electromagnetic compatibility of electronic components and systems used in vehicles, ensuring they operate reliably and without interference in the complex automotive environment. As part of the testing process, emissions and immunity assessments are usually conducted to determine how well the automotive components withstand interference and how much of it they generate. For automotive electronic systems to operate safely, dependably, and effectively, compliance with EMC standards is essential.
Why is EMC Important?
Understanding the EMC signification is crucial for ensuring electronic devices’ compatibility and minimizing interference in their functioning. EMC benefits involve ensuring device reliability and mitigating potential interference, as well as ensuring the smooth operation of electronic systems. EMC testing is critical in reducing the possibility that your device’s emitted radiation or electrical interference will interfere with nearby electronic products. It ensures that any emissions from your device remain within the product’s specified limits.
Safety Assurance
Maintaining EMC in automotive design mitigates potential issues related to electronic interference. It guarantees that electronic systems and devices function safely and consistently in the conditions for which they are designed, preventing malfunctions that might cause hazards or accidents.
Functionality
Ensures that devices function as intended without being injured by electromagnetic interference, resulting in consistent performance.
Compliance and Automotive Testing Standards
Automotive EMC standards establish the criteria and requirements for electromagnetic compatibility within vehicle electronic systems, ensuring their reliable, interference-free operation and ensuring that they meet regulatory requirements.
Electromagnetic Interference Prevention
Reduces the risk of electromagnetic interference between devices, leading to fewer interruptions and the maintenance of signal integrity in electronic systems.
Cost Reduction
Addressing EMC considerations during the design and testing phases reduces the need for costly fixes or redesigns later in the manufacturing process.
Boosting Customer’s Confidence
Enhances end users’ trust and confidence in the functionality of products by assuring them that they are reliable, secure, and won’t interfere with other devices.
The Surge of Electronics in Automotive Design
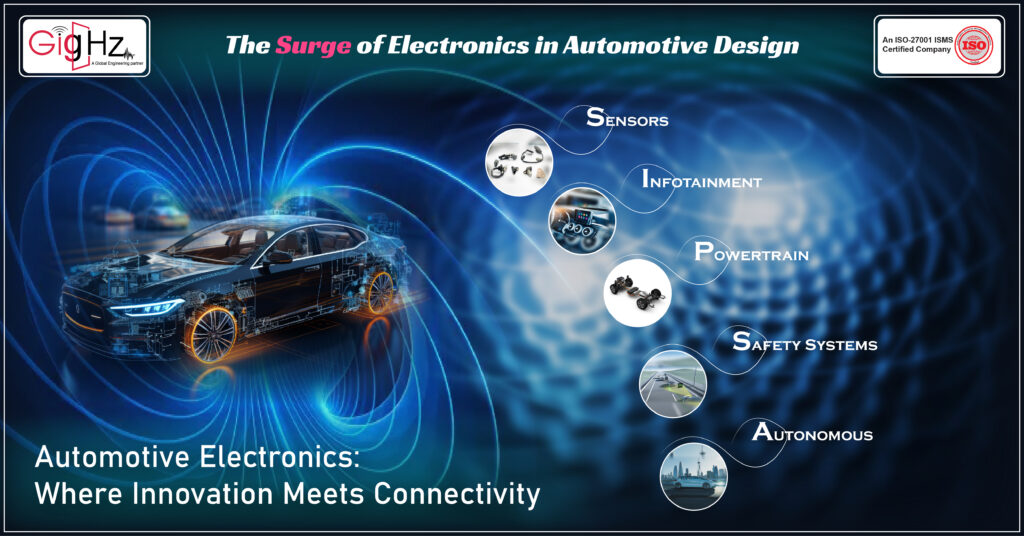
Automotive Electronics: Where Innovation Meets Connectivity
EMC in automotive electronics is critical to guarantee the seamless operation of electronic components within vehicles. The automotive industry is in the midst of a technological revolution. The rise of EMC vehicles, autonomous driving, and connected car features has ushered in a new era of automotive electronics.
Vehicles are no longer just mechanical marvels; they’re rolling data centers, packed with sensors, processors, and communication modules. As the automotive landscape evolves, so do the challenges of managing EMI, making EMC a linchpin for seamless functionality.
The Proliferation of Sensors
EMC in automotive engineering addresses the complex electromagnetic environment present in vehicles. Modern vehicles are equipped with an array of sensors for everything from collision detection to environmental monitoring. Ensuring EMC in automotive systems involves rigorous testing to prevent electromagnetic interference. These sensors are highly sensitive to electromagnetic interference, making EMC a critical factor in ensuring their accuracy and reliability. Without robust EMC measures, sensor data can become unreliable, leading to safety risks.
Infotainment and Connectivity
Infotainment systems have become a focal point in automotive design, providing drivers and passengers with entertainment, navigation, and connectivity. EMC is crucial here to prevent interference that can disrupt audio, video, and wireless communication systems. Ensuring a seamless user experience requires meticulous EMC planning and testing.
Powertrain Electronics and EMC
Powertrain electronics are the heart of modern vehicles, managing everything from engine performance to emissions control.
These systems are sensitive to electromagnetic disturbances, and EMC is essential to prevent EMI-related issues that can affect vehicle performance and efficiency.
Safety Systems and EMC
Advanced safety features like collision avoidance systems, adaptive cruise control, and lane-keeping assist rely on precise sensor data and communication between vehicle components. EMC is paramount to ensure these safety systems function flawlessly, safeguarding both drivers and pedestrians.
Autonomous Driving and EMC Challenges
The evolution of automotive EMC plays a pivotal role in the reliability of modern vehicle electronics. The advent of autonomous vehicles brings a new level of complexity to EMC. Self-driving cars rely on intricate sensor arrays and communication systems. Ensuring that these systems remain impervious to EMI is crucial for the safety of self-driving cars. EMC will be at the forefront of enabling autonomous vehicles to navigate the roads seamlessly.
EMC Challenges in the Automotive Environment

Navigating the Rough Roads of Electromagnetic Interference
The automotive environment is harsh and electrically noisy. From the electromagnetic radiation produced by spark plugs to the radio frequency interference from nearby cell towers, vehicles are subjected to a cacophony of electromagnetic disturbances.
EMC challenges are numerous, and they can impact various aspects of automotive electronics.
Radiated Emissions and Susceptibility
Radiated emissions, or the unintentional transmission of electromagnetic energy from a vehicle, can interfere with external systems and nearby vehicles.
Conversely, the vehicle itself must be immune to external electromagnetic fields to operate reliably.
EMC testing ensures that vehicles meet regulatory emission and susceptibility standards.
Conducted Emissions and Immunity
In addition to radiated emissions, conducted emissions from internal components can propagate through a vehicle’s wiring, affecting other systems.
Conducted immunity testing evaluates a vehicle’s ability to withstand electrical disturbances introduced through its power and signal lines.
High-Voltage EMC in Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Electric vehicles (EVs) bring unique EMC challenges due to their high-voltage electrical systems.
Ensuring that high-voltage components do not generate EMI that affects other vehicle systems and that the vehicle is immune to external interference is paramount for EV safety and reliability.
EMC in Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles combine internal combustion engines with electric powertrains, creating a complex electrical environment.
EMC considerations in hybrids involve managing the interplay between these two power sources while maintaining EMI compliance.
EMC Testing and Validation
Before a vehicle hits the road, it undergoes rigorous EMC testing. These tests ensure that the vehicle meets regulatory requirements and performs reliably in real-world conditions.
Testing includes emissions testing, susceptibility testing, and more to validate the vehicle’s EMC performance.
How can EMC radiation be reduced?
Improving EMC in a circuit is a big challenge. First, we need to understand how electromagnetic radiation works before we can try to lessen it. Electromagnetic radiation can bother a device in two main ways: through waves (like radio) or by electrical signals from other things nearby. Ways to protect a device from outside interference also work well to protect other devices from generated electromagnetic interference.
While EMC immunity is important, it is often best to begin with emissions, as this is the most common cause of device failure during the product testing stage. Once identified, emissions can be reduced by changing the design to emit less or incorporating methods for absorbing emissions before they reach the outside world.
EMC Solutions for Automotive Electronics

Driving Toward EMC Excellence
To address these EMC challenges, automotive manufacturers employ a range of solutions and best practices. From electromagnetic shielding to carefully designed grounding systems, EMC measures are integrated into every aspect of automotive design and manufacturing.
Electromagnetic Shielding
One of the primary methods for managing EMI in vehicles is electromagnetic shielding. Shielding involves encasing sensitive electronic components in conductive materials to contain electromagnetic energy.
Tips: Proper shielding prevents emissions and protects vehicle systems from external interference.
Grounding and Bonding
Effective grounding and bonding are essential for creating a low-impedance path for electromagnetic currents to dissipate safely. Grounding ensures that the vehicle’s electrical systems remain stable and resilient in the face of EMI.
Filtering and Ferrites
Filters and ferrite components are used to suppress high-frequency noise in vehicle electrical systems. These components play a critical role in reducing EMI and maintaining signal integrity in automotive electronics.
EMC Testing and Simulation Tools
Cutting-edge EMC testing and simulation tools allow automotive engineers to assess and mitigate EMI risks during the design phase. These tools help identify potential issues early in the development process, saving time and resources.
EMC Compliance and Standards
EMC test standards for automotive electronic components dictate the criteria and benchmarks used to assess their electromagnetic compatibility, ensuring they meet industry regulations for safe and reliable operation within vehicles.
International EMC Collaboration
Given the global nature of the automotive industry, international collaboration on EMC international standards and practices will be essential. Harmonizing EMC requirements across regions will facilitate the development and deployment of vehicles that meet consistent EMC standards worldwide.
The automotive industry is a global endeavor, with vehicles and components crossing borders regularly. International collaboration in Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is crucial to ensure that EMC standards and practices align across regions, fostering a cohesive and efficient global automotive ecosystem.
Global EMC Standards Initiatives
Numerous international bodies and organizations work to establish EMC standards for the automotive industry.
These initiatives aim to create a common framework that automotive manufacturers and suppliers can follow, simplifying compliance across different markets.
EMC Testing and Certification Harmonization
Harmonizing EMC testing and certification procedures ensures that vehicles and electronic components meet consistent standards worldwide.
This streamlines the process for manufacturers, reducing duplication of testing efforts and enabling easier market access.
Regulatory Alignment
Different regions may have distinct regulatory requirements related to EMC.
International collaboration seeks to align these regulations wherever possible, reducing compliance complexities for automotive companies and facilitating the global distribution of vehicles.
Information Sharing and Best Practices
Collaboration goes beyond standards; it involves sharing knowledge and best practices.
Forums and working groups facilitate the exchange of information, allowing experts from different regions to learn from one another’s experiences and insights.
Future-Proofing Global EMC Standards
As automotive technology evolves, global EMC standards must evolve with it.
International collaboration ensures that EMC standards remain relevant and adaptable to emerging technologies, supporting a dynamic and innovative automotive industry.
EMC Outsourcing in the Automotive Industry

Outsourcing within the field of Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is a strategic approach adopted by many automotive manufacturers. It involves enlisting the services of external experts or specialized firms to handle EMC testing and compliance for the electronic systems integrated into modern vehicles. EMC testing demands specialized knowledge, equipment, and facilities, making it a prime candidate for outsourcing.
This practice offers several advantages, including potential cost savings, streamlined processes, and increased efficiency, as automakers can leverage the expertise of dedicated EMC professionals.
Nonetheless, successful outsourcing in EMC requires meticulous management and clear communication with the outsourcing partners. It’s essential to establish robust protocols and standards to ensure that EMC compliance is rigorously maintained. This is critical because the integrity of automotive electronics directly impacts vehicle safety and performance.
Thus, while outsourcing can provide numerous benefits, maintaining a close and cooperative relationship with outsourcing partners remains paramount in preserving EMC standards and guaranteeing the quality and safety of automotive electronics.
Conclusion
Driving Toward Global EMC Harmony
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is a vital guardian for automotive electronics, mitigating electromagnetic interference (EMI) to maintain system integrity and reliability. It harmonizes the interaction between electronic components, such as the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and infotainment systems, ensuring their coexistence without disruption.
EMC safeguards against EMI-induced malfunctions that could compromise vehicle safety and performance. In essence, it’s the uncelebrated sentinel of contemporary automotive electronics, silently preserving operational stability on the road.
Hope you enjoyed this blog, right?
For more details, feel free to Contact Us and reach us at
For more details, feel free to reach us to reach us
For more details, feel free to reach us
For more details, feel free to reach us
